If you want to take a trip to Mars, now is the time to go.
Every 26 months, Mars reaches the closest point to Earth in its orbit, and the nearest launch window to the Red Planet is this summer, when launching a spacecraft will use the least amount of fuel.
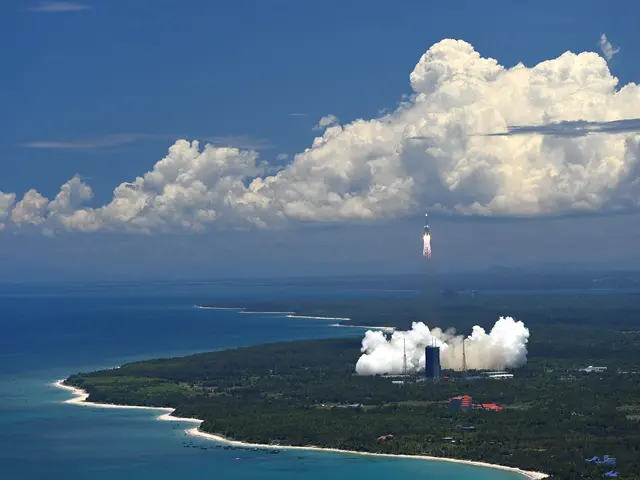
On Thursday, China launched a Mars probe, aiming to complete orbiting, landing and roving in one mission, marking the first step in its planetary exploration of the solar system.
A Long March-5 rocket, China's largest launch vehicle, carrying the spacecraft with a mass of about 5 tonnes, soared into the sky from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on the coast of southern China's island province of Hainan at 12:41 p.m. (0441 GMT) on the day.
This is China's first Mars mission named Tianwen-1. About 36 minutes later, the spacecraft, including an orbiter and a rover, was sent into the Earth-Mars transfer orbit, embarking on an almost seven-month journey to the red planet.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), China and the United States all decided to seize this summer to launch their Mars missions.
On Monday, the UAE successfully launched its 1.5-ton Hope Probe, the Arab world's first Mars orbiter, kicking off the three international missions to the Red Planet this summer.
The Hope Probe, which measures 2.9 meters in length and 2.37 meters in width, was developed at Mohammed bin Rashid Space Center in Dubai, and took off from the Tanegashima Space Center in Kagoshima Prefecture in southwestern Japan.
The probe is expected to reach Mars by 2021 to mark the 50th anniversary of the founding of the UAE.
U.S. Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is slated to launch no earlier than July 30, said the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on its official website.
The rover will take off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, and will land on the Red Planet in February 2021, NASA said.
The rover's astrobiology mission will seek signs of past microscopic life on Mars, explore the geology of the Jezero Crater landing site, and demonstrate key technologies to help prepare for future robotic and human exploration, according to NASA.
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Roscosmos Space Corporation said in mid-March that the launch of the second ExoMars mission was delayed to 2022.
Japan's Mars mission is scheduled to launch in 2024, said the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
The ESA said the scientific reasons for heading to Mars, the planet that is most similar to Earth in the Solar System, are searching for life, understanding the surface and the evolution of the planet, and preparing for future human exploration.
 简体中文
简体中文



















