By writer Prof. Engr. Zamir Ahmed Awan
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a free trade agreement among the Asia-Pacific nations. It includes Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history. The RCEP was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam and took effect 60 days after it has been ratified by at least six ASEAN and three non-ASEAN signatories.
In current geopolitics, trade is dominant. Many new alliances emerge based on economic interests and foreign policies are implemented in international relations. It seems that the biggest impact of RCEP is unity among all member countries. Some political differences have been ignored or undermined, and economic interests were given the highest priority. RCEP promotes peace and stability in the region.
Since RCEP was signed last year, the trade among member states has witnessed a positive and encouraging increase. More trade means more interactions, more understandings, more harmony, more peace and stability, which lead to collective prosperity. The future belongs to this region and RCEP will positively play its due role.
When the RCEP was signed, Chinese premier Li Keqiang declared it “a victory of multilateralism and free trade”. Singaporean prime minister Lee Hsien Loong called it “a major step forward for our region” and a sign of support for free trade and economic interdependence. Many other well-known analysts predicted that it would help stimulate the economies of signatory nations amid the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as “pull the economic center of gravity back towards Asia, with China poised to take the lead in writing trade rules for the region”, leaving the U.S. behind in economic and political affairs.
Under Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China has been helping regional countries to develop infrastructure, promoting connectivity and people-to-people contacts, paving ways for more economic activities. BRI is instrumental for socio-economic developments in the region. RCEP and BRI are interlinked and support each other directly or indirectly.
Pakistan is one of the biggest beneficiaries of BRI. China-Pakistan economic corridor (CPEC) is one of the six planned economic corridors under BRI. It is a flagship project and in the most advanced stage. The net impact on Pakistan’s economy, CPEC contributes to almost 2 percent growth in GDP approximately. Pakistan was an energy deficient country and was facing a severe shortage of electricity, almost facing load-shedding up to few hours on daily basis. But, under CPEC, several power projects have been completed and the deficiency of electricity has almost been overcome. Few more are still underway, it is expected that after the completion of all these power projects, Pakistan will produce more electricity. Yet, some more are in the pipeline to meet the future needs of the country.
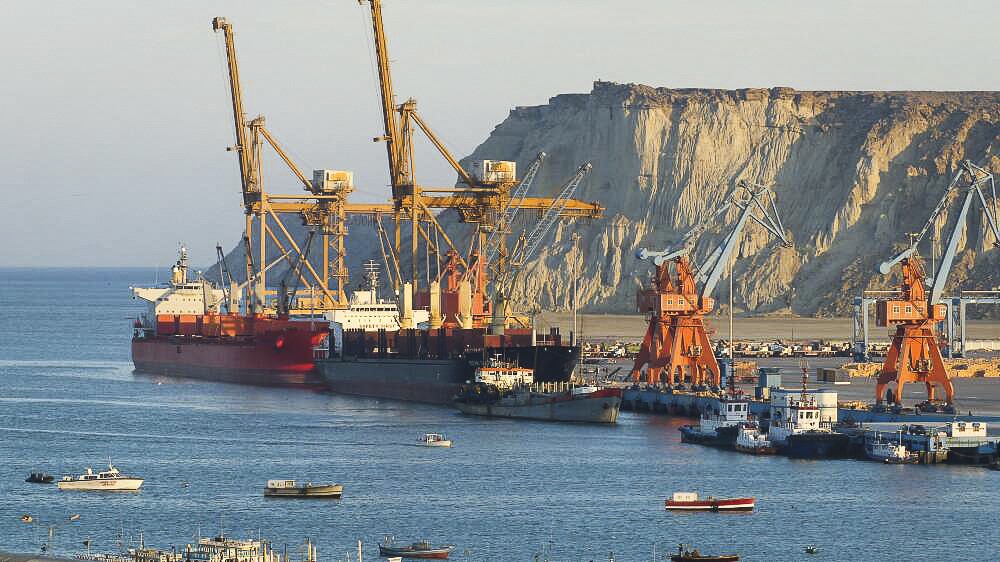

A broad-based network of roads has been set up in the breadth and width of the country, making connectivity among far-flung areas of Pakistan. It has improved transportation of passengers as well as cargo, leading to enhanced economic activities. Roads have a positive impact on the economy and social life in Pakistan.
Jobs have been created in Pakistan, and youth, especially fresh graduates are the direct beneficiary of CPEC. Chinese investments have surpassed any other countries’ investments in Pakistan.
CPEC has entered into the next phase, where industrialization, agriculture, social sector, and health are priorities. It is expected this phase will be more useful for Pakistan in terms of more investment, transfer of technology, job creation, rapid industrialization, modernization of agriculture, and better health care facilitation.
With the changing situation in Afghanistan, BRI is vital for Afghanistan and Iran. An extension of BRI to Afghanistan and Iran will integrate with CPEC and boost the benefits of CPEC. BRI is the guarantor for regional connectivity, trade, and developments. China has a strong will, sufficient experience, and enough resources to make BRI a success story for the rest of the world to follow similar initiatives.
The construction of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area is a major national strategy of China. Southern China is technically and economically more advanced. There are more opportunities of trade. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, will become a hub of commercial activities and will contribute more in national and regional economy. It is expected that Guang Dong province will become leader in technical and economic developments in the near future. The impact of trade and economy will help local people to have much higher standard of life.
(ASIA PACIFIC DAILY)
 简体中文
简体中文

