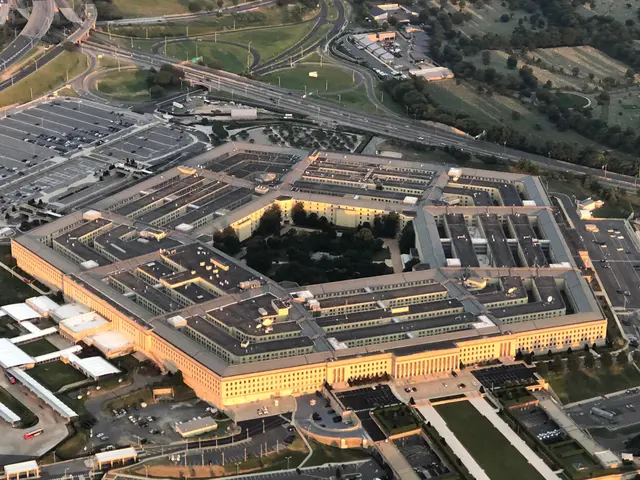
Countries across the globe, including the United States, make every effort to safeguard national security and ensure the fundamental basis for their stability and development.
The United States has in recent decades taken a series of steps to strengthen national security through legislation and law enforcement.
The National Security Act of 1947 provides a legal basis for the U.S. government to craft foreign policy and establish military organizations, and has been a constant source of strengthening America's national security over the years.
The National Security Council (NSC) is among the institutions that presidents use to handle long-term problems and more immediate national security crises. The NSC includes the president, vice president, secretary of state, secretary of defense, and the director of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
For instance, then President Dwight D. Eisenhower used the NSC meetings to make key foreign policy decisions, while John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson preferred to work more informally through trusted associates.
To achieve the act's stated goal of providing a comprehensive program for future national security, the former Department of War and the Navy Department merged into the Department of Defense, which also includes the Departments of the Army and Air Force.
As it also serves to coordinate national security with the intelligence community and its many capabilities, the legislation created the CIA, the government's primary civilian intelligence-gathering organization, and established the position of director of central intelligence (DCI).
The Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 established the director of national intelligence (DNI), a U.S. government cabinet-level official, to replace the DCI as head of the 17-member U.S. Intelligence Community.
After the 9/11 terrorist attacks, the U.S. Congress greenlighted the Patriot Act, which covers Section 215, one of the most controversial programs for domestic and international surveillance.
The section, officially called the "business records" provision, authorized the National Security Agency's (NSA's) bulk collection of telephone metadata - information that includes who called whom when, but not what was said.
In June 2015, then President Barack Obama signed the USA Freedom Act, which includes a new surveillance program aimed at ending more than a decade of bulk collection of telephone records by the NSA.
But it makes records already held by telephone companies available for broad searches by government officials with a court order.
 简体中文
简体中文