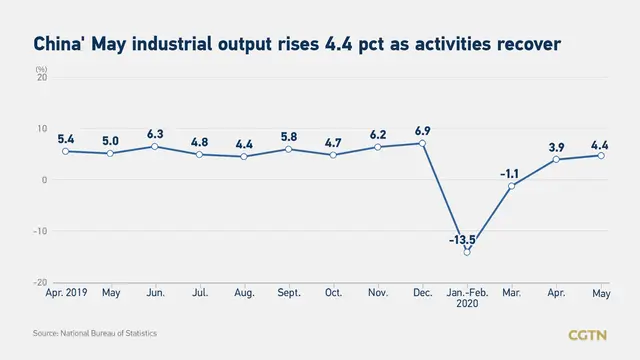
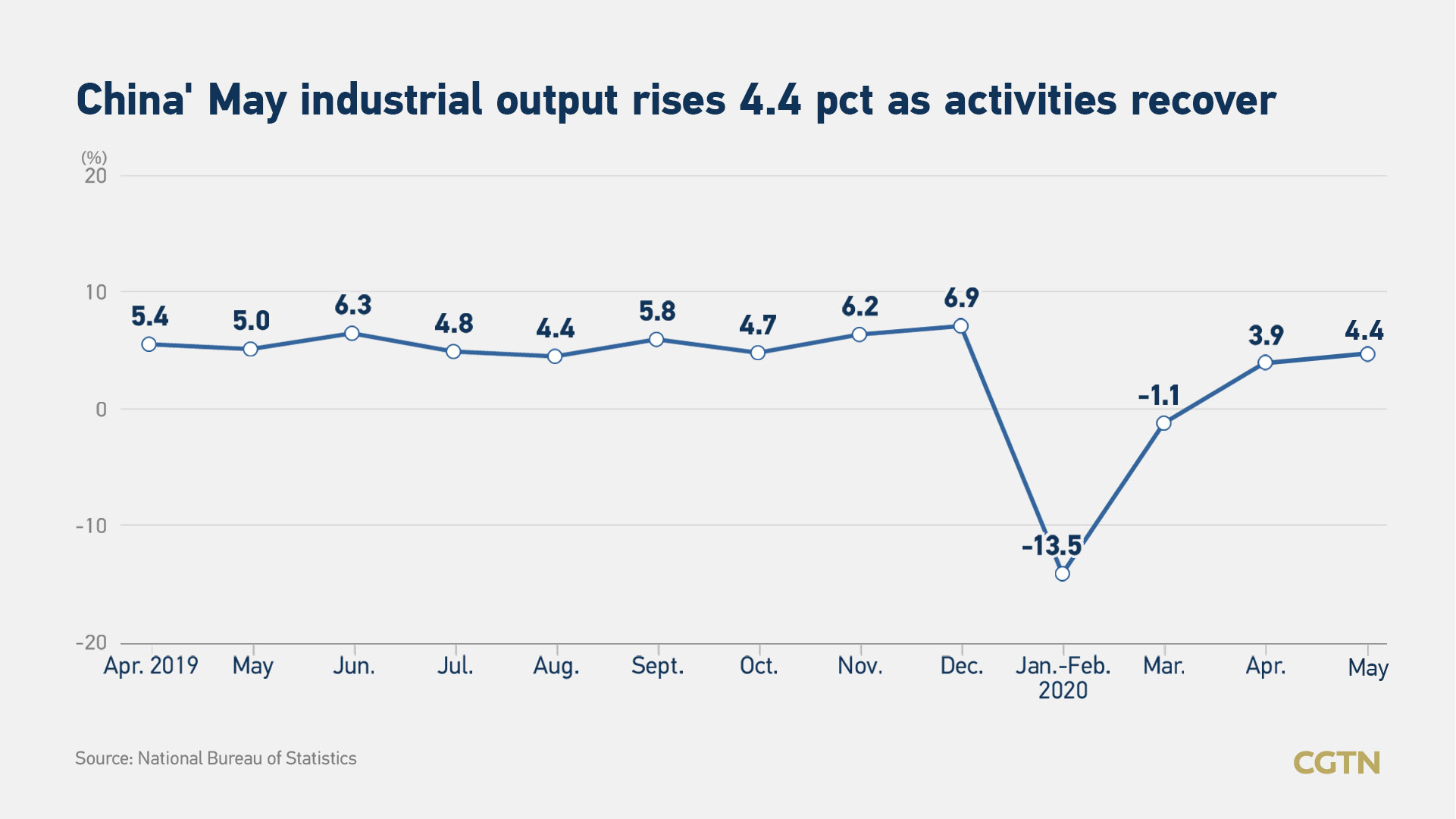
China's value-added industrial output expanded 4.4 percent year on year in May, but retail and investment stayed negative as economic recovery continues amid COVID-19 control, official data showed on Monday.
Industrial output, a gauge of manufacturing, mining and utilities sector activity, was up from 3.9 percent growth in April, but slightly below the forecast of five percent by the Bloomberg and Reuters polls of analysts. Within it, manufacturing grew by 5.2 percent, mining was up 1.1 percent and utilities by 3.6 percent, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS).
"It should be noted that the overseas epidemic and the global economy have become more complicated. The stable operation of the domestic economy still faces many risks and challenges," NBS said in an online statement.
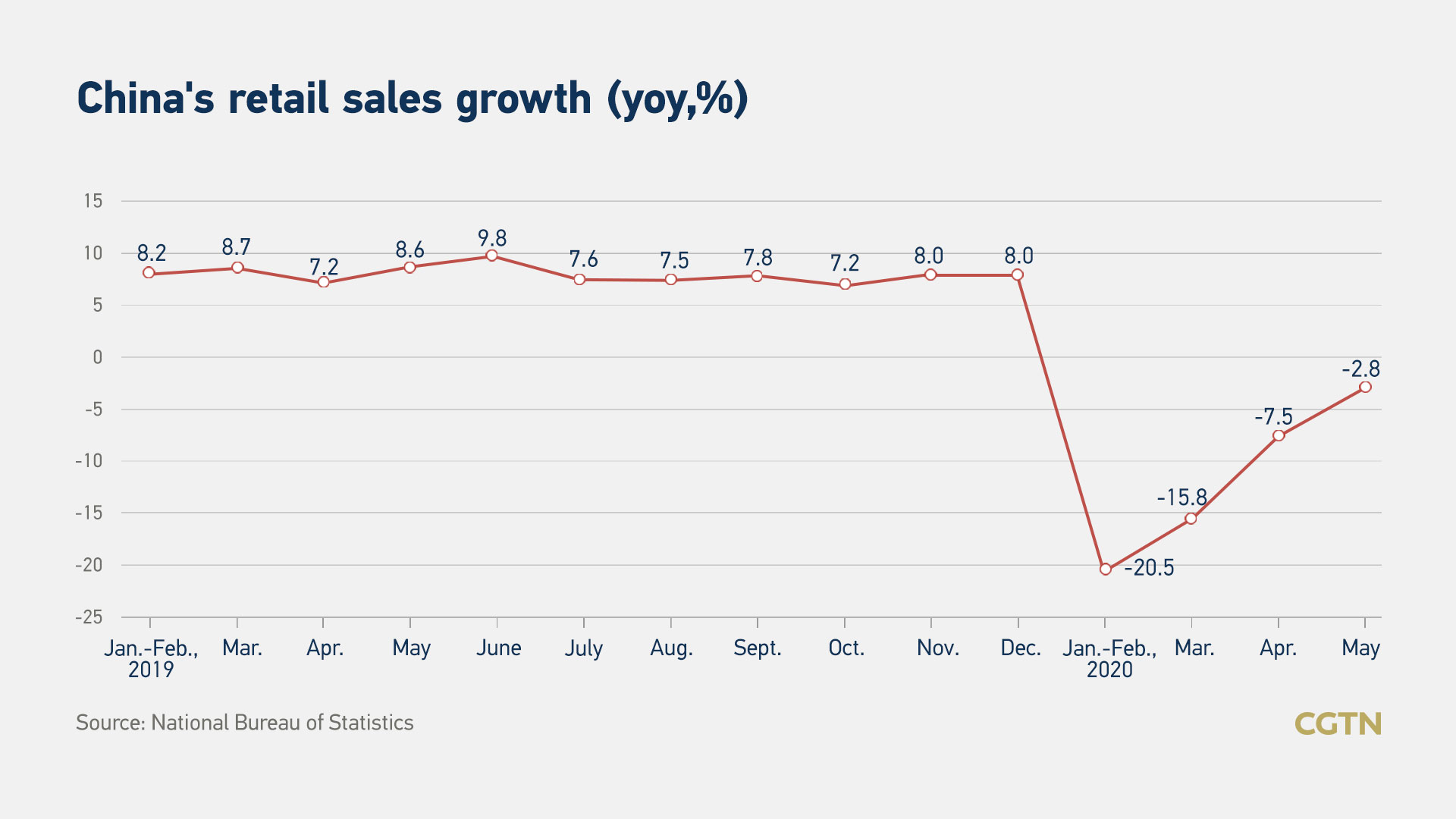
Retail sales, a crucial indicator of consumption in the world's biggest consumer market, fell 2.8 percent year-on-year, more than a predicted decline of two percent by Reuters.
Fixed asset investment, the year-to-date value of spending on real estate, infrastructure and capital equipment, dropped 6.3 percent between January and May from the same period last year, worse than a forecast fall of 5.9 percent by Reuters.
However, both retail sales and fixed asset investment pointed to some signs of recovery, as they were better than April's reading of minus 7.5 percent and minus 10.3 percent respectively.
Investment in infrastructure, manufacturing and real estate edged down separately 6.3 percent, 14.8 percent and 0.3 percent year on year in the first five months of the year, narrowing from the decline of 11.8 percent, 18.8 percent and 3.3 percent between January and April.
The job market remained generally stable in May, with the surveyed unemployment rate in urban areas standing at 5.9 percent, down 0.1 percentage points from the previous month.
The NBS canceled its press conference on Monday, instead releasing the economic data online due to epidemic control efforts.
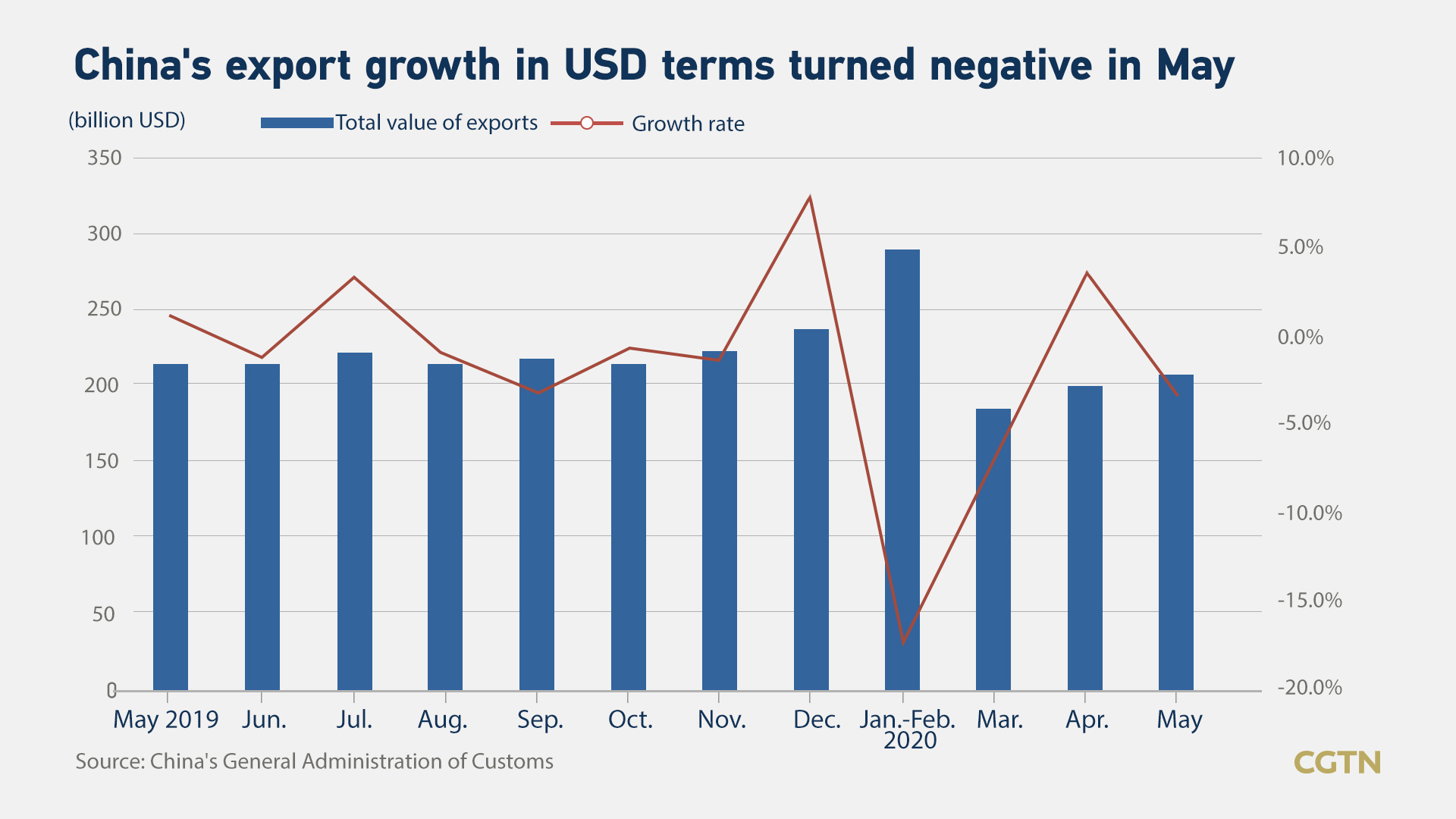
Export growth turns negative
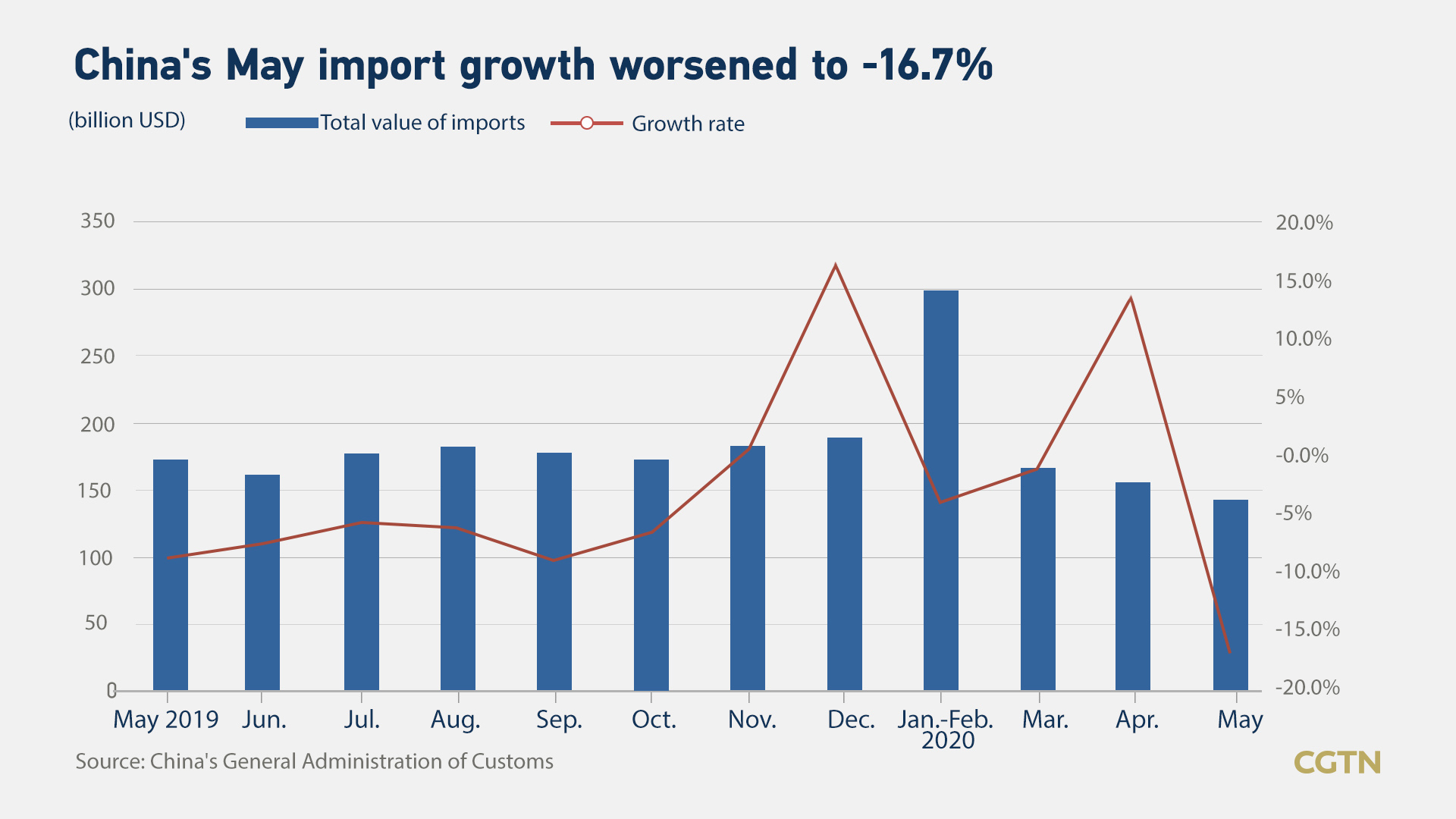
The country's May exports contracted 3.3 percent year on year in U.S. dollar terms as the flare-up of infections still devastates demand, while a deeper fall of 16.7 percent in imports pointed to mounting pressure facing the manufacturing sector.
"The sharp decline of commodity prices was to blame, dragging down import value of crude oil to by 55 percent, while its import volume jumped notably by 27 percentage points to 19 percent. Import volume of iron ore and copper ore both dipped in May, possibly indicating soft related domestic demand," UBS said.
In contrast, import growth of agricultural goods picked up by 6 percentage points to settle at 12 percent, with a marked gain in soybean and grain, both up by 40 percentage points to reach 25 percent and 29 percent, respectively.
China's export growth turns negative but still beat May expectations
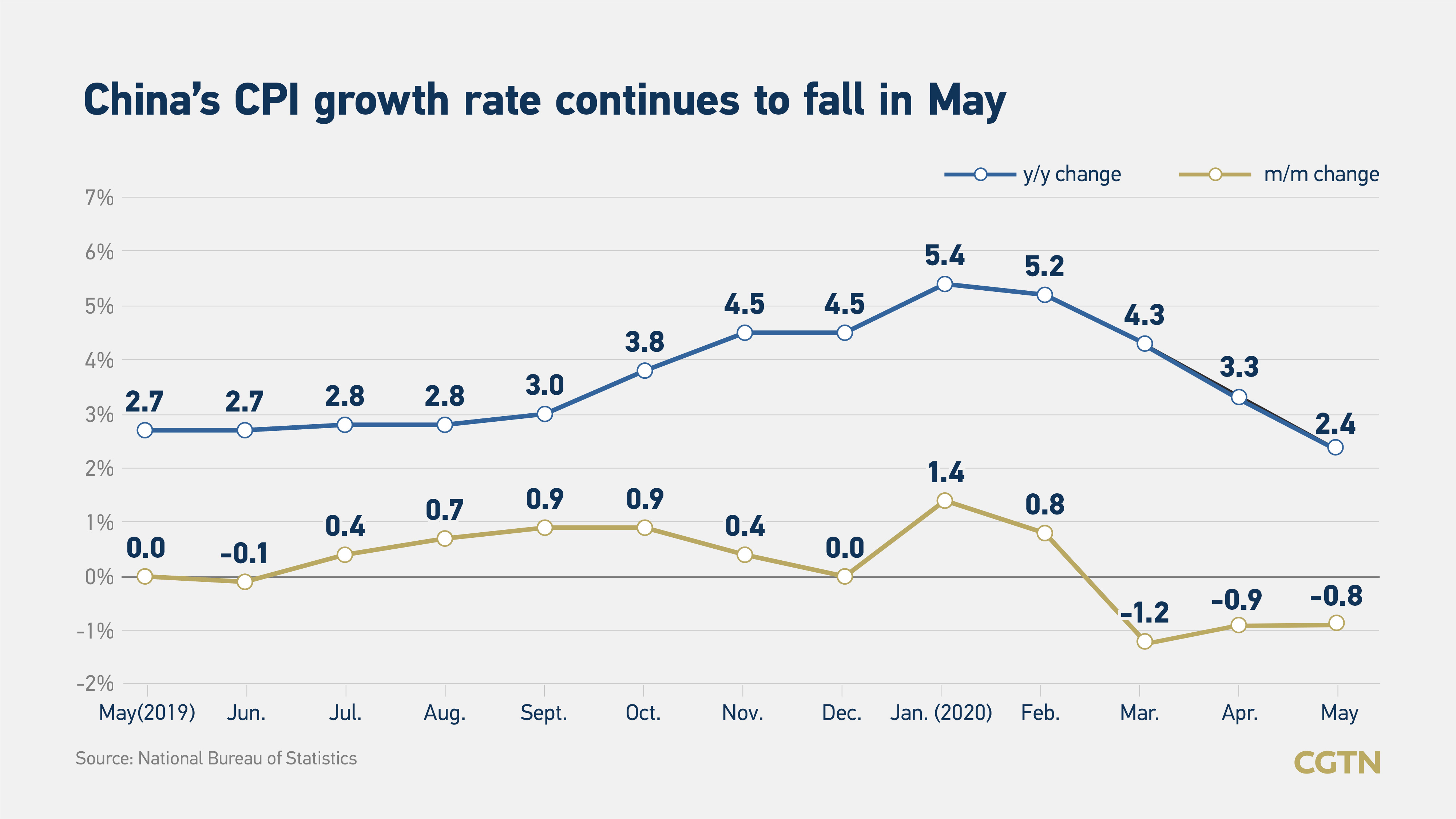
CPI growth continuously falls back
China's inflation further sailed into the slowdown territory in May, with its main gauge of the consumer price index (CPI) registering a year-on-year rise of 2.4 percent, 0.8 percent narrower than in April, weighed by a drop in food prices. The reading was lower than the 2.7 percent increase estimated by a Reuters poll and Nomura Securities.
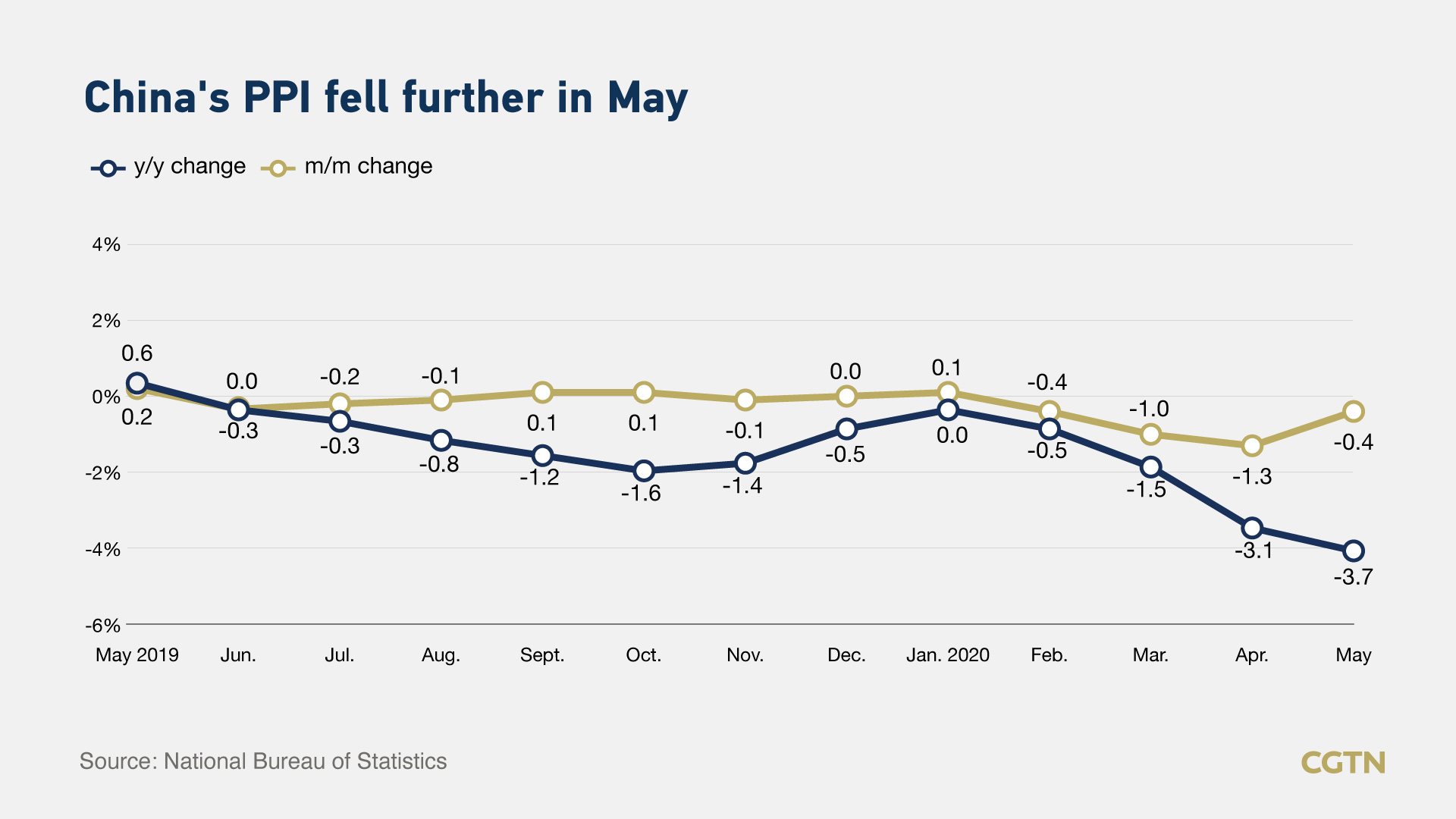
The producer price index (PPI), which measures costs for goods at the factory gate, shed 3.7 percent from a year earlier in May, as compared to a median forecast for a 3.3 percent contraction tipped by a Reuters poll of analysts and a 3.1 percent fall in April.
Uptrend in credit growth continues
May's money and credit data were a mixed bag, but the uptrend in credit growth continued, according to Nomura Securities. New yuan loans dropped from 1.7 trillion yuan in April to 1.48 trillion yuan in May, weaker than expected 1.5 trillion yuan by Reuters and 1.8 trillion yuan by Nomura Securities. Meanwhile, new aggregate financing ticked up to 3.19 trillion yuan in May from 3.09 trillion yuan in April, lower than Nomura's prediction of 3.4 trillion yuan.
GDP growth forecast
"We recently raised our year-on-year real GDP growth forecast in the second quarter to 1.2 percent from minus 0.5 percent and cut our GDP growth forecasts in the third quarter and fourth quarter to 4.5 percent and five percent respectively from 5.8 percent. Consequently, we cut our 2020 annual GDP growth forecast to 1.3 percent from 1.5 percent. We maintain our 2021 GDP growth forecast at 8.8 percent," Nomura Securities said in its latest research report.
 简体中文
简体中文